Yves here. This post gives a sense of how many people globally are vulnerable to the coronavirus shock.
By C.P. Chandrasekhar, Professor of Economics, School of Social Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, India and Jayati Ghosh, Professor of Economics and Chairperson at the Centre for Economic Studies and Planning, School of Social Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, India. Republished from Network IDEAs; originally published in the Business Line on March 24 2020
The global devastation caused by Covid-19 is only just beginning, with the severe threat to public health worsened by the evident inability to cope of most health systems across developing and developed countries. Many states across the world appear to have realised the serious potential of this pandemic and have declared lockdowns, closures, partial curfews and curtailment of all but essential activities in efforts to contain the contagion.
The economic impacts of such lockdown are also just beginning to be felt, and will escalate in the coming months. The discussion on the economics of this pandemic has tended to focus on supply disruptions and the likely financial losses of companies, especially those in travel, transport and other services and manufacturing activities. Precisely because companies have more lobbying power and more political voice in general, they have already started clamouring for (and being offered) incentives, bailouts and other relief measures to allow them to cope with this crisis.
But in fact, the worst material impacts are already being felt by informal workers, who face a dismal spectrum of probabilities of loss of livelihood, from declining earnings among the self-employed to job losses among paid workers. These are likely to get much worse in the coming months. Even so, barring in just a handful of countries, very few governments have declared strong measures to cope with these effects—and therefore they are letting loose forces that could be even more devastating for poor people across the world. In the worst-case scenario, this could even mean that more people could die from hunger and the inability to treat other problems than will do so because of the virus.
Just how seriously should we take the concerns of informal workers alone? The answer partly depends on how extensive the problem is. The ILO considers a worker to be informal if s/he is a worker whose social security is not paid for by the employer, is not entitled to paid annual leave and paid sick leave; or works in a household; or owns and runs an informal enterprise, typically in the form of self-employment, but also including micro-enterprises. Figure 1 shows that, according to the ILO, 61.2 per cent of all employment was informal, and most of this was also in informal sector enterprises that rarely if ever get the benefit of any government subsidies or protection even in periods of crisis. This is less of a problem in developed countries, where employment is still dominantly formal. In the emerging and developing countries as a group, informal workers account for as much as 70 per cent of all employment, so two out of every three workers are informal.
Figure 1: Informal workers form the bulk of total employment across the world
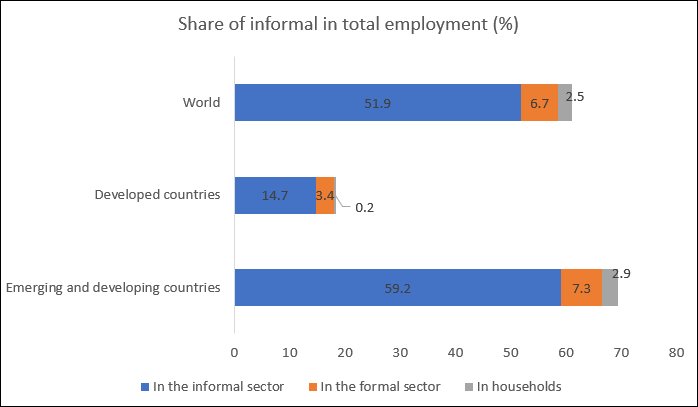
Source for all figures: Women and Men in the Informal Economy: A Statistical Picture, Geneva: ILO, 2018.
In the aggregate, the number of informal workers came to as many as 2 billion globally in 2018, and is likely to have gone up slightly since then. These are workers who lack most rights at work, decent working conditions and most forms of social protection except whatever minimal amounts may be provided by the state. They and their families are clearly the most vulnerable to any economic downturn. When such a downturn comes in the wake of an unprecedented public health calamity, the concerns are obviously multiplied.
Figure 2: Men and women workers face similar extent of informality
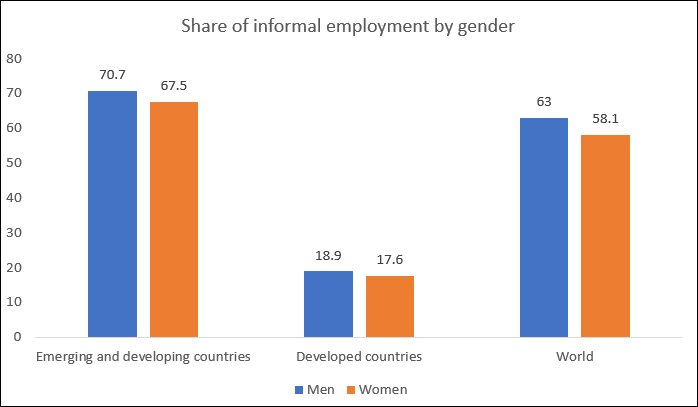
Figure 2 indicates that men are marginally more likely to be informal workers than women, possibly because several public services tend to hire more women. The notion that informality is higher in developing countries because of the greater significance of agricultural employment is dispelled by Figure 3. It is sometimes argued that farmers do not need the same safety nets as other workers and can survive even in critical economic conditions because of the nature of their activity. This is no longer true given the interconnectedness of economies, and agriculturalists very much also need bailout packages specific to that sector. But in any case, even in non-agricultural activities, informal workers predominate in the Global South, to the extent of making up 60 per cent of all such workers.
Figure 3: Informality is high even in non-agricultural activities
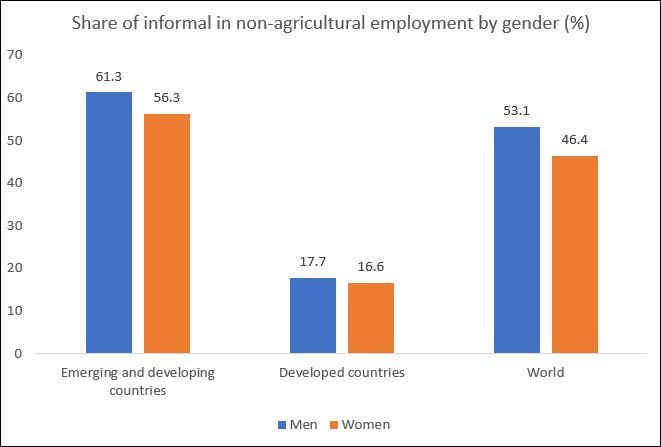
Figure 4: India has one of the highest rates of informality in the developing world
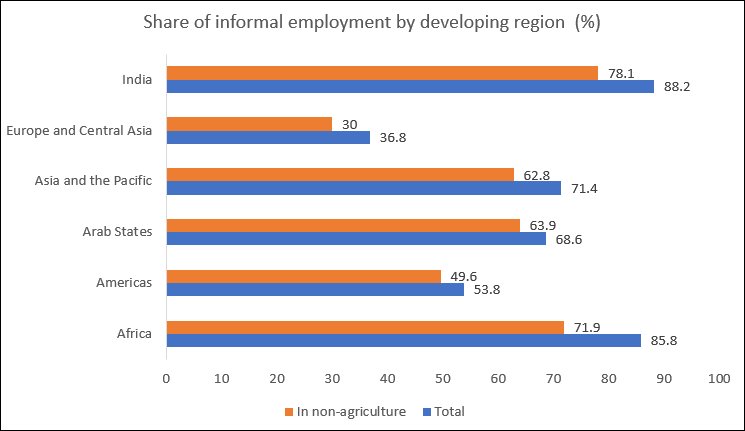
Even in the developing world, there are significant variations across regions, as Figure 4 indicates. What is striking is that India—which seems to be on the verge of a very substantial spike in Covid-19 cases, has a very large population and is poorly equipped to deal with an epidemic of such proportions—has one of the highest rates of employment informality in the developing world, much higher than the average of Asia and the Pacific or African countries.
It is obvious that if the human suffering caused by this pandemic is to be minimised or reduced, both public health measures and safety net policies have to recognise this reality. It is not enough to recommend or even try to enforce the poorly phrased “social distancing” (more properly physical distancing) if people’s conditions of work and life simply do not allow it. Containment policies have to provide the infrastructure and facilities that would enable people to follow those rules: at the minimum, the wherewithal for cleanliness (like adequate clean water and soap) and ensuring physical distance. Also, to enable such workers and their families to follow rules that would minimise contagion, and survive both the possible onslaught of the disease and extreme loss of livelihood over this crisis period, income support and food provision are essential. In many developing countries like India, free public provision of basic food items (some of which are already supplied by the public distribution system) and time-bound cash transfers to all those who are not formally employed would be important measures for this.
The necessary measures will vary by country, but everywhere, governments have to go beyond compensating companies, to focussing on the urgent needs of informal workers.


Thanks for mentioning this. As I watched the lines of people trudging along India’s roads leading out of the cities back to “home” I couldn’t help wondering “what was the govt/tv thinking ? don’t they know where the slum-dwellers come from, where the city apartment, road, office block construction labourer comes from, where the street-vendor comes from ?”
What’s an early question people ask each other: “Where are you from ?” Haven’t the govt. bothered to ask ? And never mind that – look at the agitation in major cities of local people AGAINST migrants from the poorer states like Bihar .
That should have given the govt a clue. This article captures the people, issues behind those sad images well:
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/coronavirus-india-covid-19-migrants-walking-6341071/
Excerpt:
In a way its akin to how the elite in the US too imagine what the USA is composed of.
This is all very sad – a massive failure of imagination – or even just asking the question ” where are you from.. ” to the local tea-boy, the street vendor, let alone overhearing the language they use with each other.
Possibly the Indian government knew exactly what would happen.
On the other hand, food is often more available in villages, along with a greater possibility of social distancing. Not that I’m defending India’s policies or the way they’re being implemented, but having millions cramped together in slums at this time may be the worst of the alternatives.
Many of the developing countries get a not insignificant (for them) amount of money through remittances from citizens working abroad. Those citizens are rarely in secure and well-paying jobs (possibly instead in informal jobs) so there is a risk that remittances might dry up. The senders and recepient both tend to be un-banked and therefore use the more expensive way of transferring money.
The big remittances firms might soon have an indication of how big (if any) effect the shutdown in the developed nations might have on the less developed nations.
My thinking, in time of isolation it that we should stop the clock for many (most?) payments, particularly when isolation makes income go to 0. Common sense isn’t it?